Ergothioneine Supplement:Nature’s Powerful Anti-Aging Ingredient
When it comes to antioxidants on the market today, many of them claim to support the immune system. Ergothioneine is one of the oldest biologically active ingredients. Ergothioneine is not produced in the body, it must be obtained through diet.
Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring antioxidant that has gained attention in recent years for its potential health benefits. Found in certain dietary sources like mushrooms, it's been studied for its role in protecting cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the potential benefits of ergothioneine supplements, explore the current research surrounding its use, and discuss recommendations for dosage and timing.
Science has never been conclusive, but the leading hypothesis regarding the origin of ergothioneine (EGT) is that it actually predates the oxidation of Earth's atmosphere, which, if true, would make it about 2.4 billion years old. This would undoubtedly make ergothioneine (EGT) one of the oldest biologically active compounds known to science.
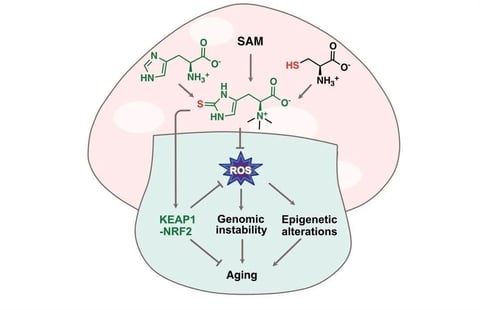
Given this, it is not surprising that human cells exhibit a high affinity for ergothioneine (ET)—a substance that has accompanied us essentially throughout our evolutionary history.
It’s no surprise that ergothioneine (EGT) plays an important supporting role in many aspects of human health.
Ergothioneine (ET) is an antioxidant found naturally in a variety of uncommon foods, especially edible mushrooms.
A number of compelling studies have shown that ergothioneine (EGT) can provide profound protection against oxidative stress, improve immune and inflammatory function, and protect cells from many different types of cytotoxins, especially in the skin , of course, the skin health benefits are really just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to ergothioneine applications.
The existence of an evolutionarily conserved ergothioneine-specific cellular transporter strongly illustrates the importance of this molecule to human longevity.
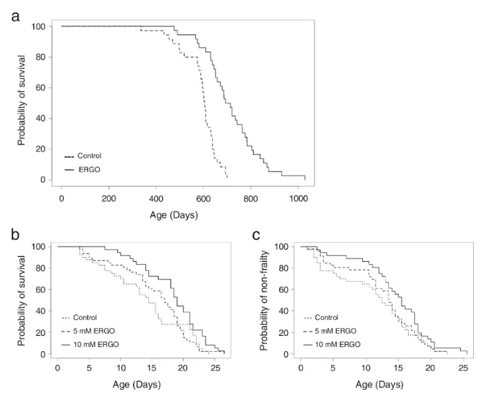
Oral administration of ergothioneine significantly extends lifespan in mice
On March 6, 2024, Professor Yukio Kato from Kanazawa University School of Pharmacy in Japan published an article titled "Ergothioneine promotes longevity and healthy aging in male mice" in the magazine "GeroScience".
The study found that ergothioneine supplementation extended lifespan and promoted healthy aging in mice. The study pointed out that the median and average survival ages of mice fed ergothioneine at a dose of 4-5 mg/kg body weight per day increased by 16% and 21% respectively.
In addition, the study also found that treatment with ergothioneine at a concentration of 10 mM could significantly extend the lifespan of C. elegans and improve the non-senescence period.
The conclusion of this paper shows that the intake of ergothioneine can inhibit the aging process of multiple organs such as the kidneys, liver, and brain, and improve age-related learning and memory impairments.
Potential Benefits of Ergothioneine Supplements
Antioxidant Properties:Ergothioneine acts as a potent antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage to cells. This protective effect may help prevent various chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress, including cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.
Anti-inflammatory Effects:In addition to its antioxidant properties, ergothioneine exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. By modulating inflammatory pathways, it may help reduce inflammation throughout the body, which is linked to numerous health conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Skin Health: Ergothioneine has been investigated for its potential benefits in promoting skin health. Studies suggest that it may protect skin cells from UV-induced damage, thereby reducing the risk of premature aging and skin cancer. Additionally, ergothioneine's antioxidant properties may help maintain skin elasticity and hydration.
Immune Support: Some research suggests that ergothioneine may support immune function by enhancing the activity of immune cells and reducing inflammation.By bolstering the body's defenses, it may help reduce the risk of infections and support overall immune health.
Neuroprotective Effects:Preliminary studies have explored the potential neuroprotective effects of ergothioneine in the context of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. While more research is needed, early findings suggest that ergothioneine may help protect neurons from oxidative damage and inflammation, potentially slowing the progression of these conditions.
Current Research on Ergothioneine
While the potential benefits of ergothioneine are promising, much of the research is still in its early stages. Several studies have investigated its effects in cell cultures, animal models, and human trials, but more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential.
How Much Ergothioneine Does The Human Body Need To Take In
Dosage and Timing Recommendations
As of now, there is no established Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) or Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) for ergothioneine. Since ergothioneine is not considered an essential nutrient, there are no formal guidelines for its supplementation. However, some ergothioneine supplements are available on the market, typically in the form of capsules or tablets.
No one has an exact answer to this question, but a comparative analysis of nutritional status across countries can help us understand the physiologically appropriate range of ergothioneine (EGT) intake.
An article published in the Journal of Nutritional Sciences in 2020 pointed out that the United States, a country with a higher incidence of neurological diseases, has lower ergothioneine (EGT) intake than countries with similar levels of economic development.
For example, Italians consume approximately 4.6 milligrams of ergothioneine (EGT) per day from food, while Americans consume only 1.1 milligrams. Of the countries examined in this study, Italy had the highest EGT intake and the United States had the lowest, so 1.1 mg to 4.6 mg is a reasonable range for adequate EGT intake.
Understanding Ergothioneine
Ergothioneine (ET) is a sulfur-containing amino acid derivative that is produced by certain microorganisms, plants, and fungi, including mushrooms. It's particularly abundant in species such as shiitake, oyster, and king oyster mushrooms. While humans cannot synthesize ergothioneine, it's absorbed from the diet and accumulates in various tissues and organs, particularly those exposed to oxidative stress.
Science has never been conclusive, but the leading hypothesis regarding the origin of ergothioneine (EGT) is that it actually predates the oxidation of Earth's atmosphere, which, if true, would make it about 2.4 billion years old. This would undoubtedly make ergothioneine (EGT) one of the oldest biologically active compounds known to science.
Given this, it is not surprising that human cells exhibit a high affinity for ergothioneine (ET)—a substance that has accompanied us essentially throughout our evolutionary history.
It’s no surprise that ergothioneine (EGT) plays an important supporting role in many aspects of human health.
Is Ergothioneine Supplement Safe
So far, no research team has published findings on ergothioneine supplement (EGT) toxicity in animal studies.
Safety trials of ergothioneine (EGT) have given rodents high doses of 1,500 mg and 1,600 mg per kilogram of body weight per day without a significant increase in mortality.
For reference only, the human equivalent dose for these doses is approximately 250 mg/kg/day. This is equivalent to a daily dose of 17 grams of ergothioneine (EGT) for 150 people (68 kg).
Regardless, both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Union's EFSA Dietary Products, Nutrition and Allergy Panel (NDA) have ruled that ergothioneine (EGT) supplements at a daily dose of 10 mg are safe for human use.

