Melatonin is a hormone substance that is produced by amine hormones in mammals and amine hormones in the human pineal gland. It is a substance that has many benefits for our human body and is worth using in our lives. But there seems to be some confusion on if melatonin really work, how much melatonin dosage you should take and how much is too much, and who can not use melatonin supplements. Studies found that common 0.1~0.3mg is safe for human body.
Melatonin can make the melanin-producing cells in our body glow, so it is called melatonin. It has many functions. It can delay aging, improve our sleep, inhibit the formation of tumors, and can also play a role in assisting the treatment of tumors. In addition, melatonin can also enhance our immunity.
How Melatonin Helps Us Sleep
The Nightly Secret of the Pineal Gland
In the mystical realms of your brain lies a tiny, pinecone-shaped gland called the pineal gland. Nestled in the center, it may be small, but it holds a powerful secret that orchestrates one of our most cherished states—sleep. This secret is none other than melatonin, the sleep-inducing elixir.
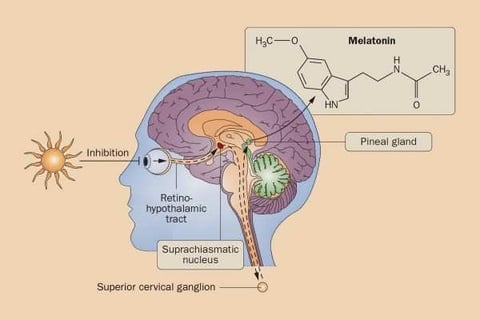
The Sunset Signal
As the day winds down and the sun begins its descent, your eyes capture the diminishing light. This gradual fade of daylight sends signals through the optic nerves to a master clock in the brain, known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). The SCN is like the conductor of a grand orchestra, setting the tempo for your body’s internal rhythms, known as circadian rhythms.
As darkness deepens, the SCN sends a whispering signal to the pineal gland: "It's time." This is the cue for the pineal gland to start its nightly ritual of melatonin production.
The Dance of Melatonin Molecules
In response, the pineal gland gets to work. It converts the amino acid tryptophan into serotonin, a neurotransmitter that is then transformed into melatonin. As evening turns into night, melatonin levels in your bloodstream begin to rise, peaking in the middle of the night. These melatonin molecules then embark on a journey through your blood, finding their way to various parts of your body, including your brain.
Melatonin’s Soothing Embrace
When melatonin reaches your brain, it binds to specific receptors, like a key fitting into a lock. This binding action sends messages to your brain, gently nudging it towards sleep. Melatonin helps reduce the alertness of your neurons, slowing down brain activity, and lowering body temperature—all of which are essential for the onset of sleep.
The Magic of the Night
As melatonin works its magic, you start to feel drowsy. Your eyelids become heavy, your breathing slows, and a warm wave of calmness washes over you. This is melatonin, serenading you into a restful slumber, ensuring that your body gets the restorative sleep it needs to function optimally.
The Break of Dawn
As dawn approaches, the first light of day touches your eyes, even through closed lids. This light sends a new message to the SCN, signaling the pineal gland to taper off melatonin production. As melatonin levels drop, your body starts to wake, ready to embrace the new day with renewed energy and vigor.
How Melatonin Helps Us Sleep
Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Melatonin aligns your sleep patterns with the natural day-night cycle, helping you feel sleepy at night and alert during the day.
Sleep Induction: By binding to receptors in the brain, it reduces neuronal activity, creating a sense of calm and promoting the onset of sleep.
Environmental Adaptation: Melatonin supplements can assist in resetting your internal clock when disrupted by jet lag or shift work, helping you adjust to new time zones or irregular schedules.
The Secretion of Melatonin is Deeply Affected by Two Factors
Circadian rhythm
Generally speaking, melatonin secretion decreases during the day and gradually increases at night.
The secretion level of melatonin at night directly affects the quality of a person's sleep. If the circadian rhythm is out of balance, it may lead to abnormal melatonin secretion.
Changes with age
The older you get, the less melatonin you secrete. The melatonin secretion of the elderly is only one-tenth of the peak, so they are more likely to have sleep disorders.
Melatonin Dosage for Adults and for Kids
According to the Food and Drug Administration of the Ministry of Health and Welfare, melatonin is a drug and must be evaluated and diagnosed by a doctor before it can be prescribed. However, in the United States and Hong Kong, melatonin is a general health food.
A US study suggests that melatonin can be taken 30 minutes before bedtime, starting with a dose of 0.5 mg. If the effect is not good, it can be gradually increased to 1-4 mg, but not to exceed 5 mg.

Who Should Not Take Melatonin
The following groups are not suitable for taking melatonin:
Pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers;
Women preparing for pregnancy, because melatonin will inhibit ovulation;
People taking birth control pills should not take melatonin, as it will increase the side effects;
People with autoimmune diseases: such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, etc.
People with depression;
People with liver and kidney dysfunction;
People taking specific medications: blood-diluting drugs (anticoagulants), immune system-suppressing drugs (immunosuppressants), diabetes-related drugs, etc.
How to Take Melatonin Naturally
Tryptamine Supplement

The source of melatonin is an amino acid called tryptophan. However, the human body cannot synthesize tryptophan on its own and must obtain it from food.
High-protein foods contain more tryptophan. According to the Food and Drug Administration's "Nutrient Database", common natural tryptophan foods are as follows: chicken breast, pork loin, salmon, edamame, pumpkin seeds, beef short ribs, oatmeal, eggs, traditional tofu, whole milk.
Vitamin B6 Supplement
Melatonin requires vitamin B6 to be synthesized, so you should also supplement with vitamin B6 foods, such as chicken breast, pork loin, salmon, tuna, bananas, bell peppers, sunflower seeds, papaya, broccoli, etc. You can also take vitamin B6 orally.
Increase Melatonin Secretion From Daily Life
Sunbathing: Get enough sun for 30 minutes during the day. After 14 to 16 hours of sunbathing, the pineal gland in the brain begins to secrete melatonin. If you go to bed at 11 pm, it is best to go to the sun between 7 and 9 am.
Go to bed early: Avoid nighttime activities as much as possible, because melatonin is secreted most vigorously from 11pm to the early morning of the next day.
Don’t use 3C before going to bed: use your phone, watch TV, use your computer, etc. These blue light and electromagnetic waves will also affect the secretion of melatonin.
Avoid smoking and drinking.
Conclusion
Melatonin powder is a valuable tool for regulating sleep-wake cycles and promoting better sleep, especially in cases of insomnia, jet lag, or shift work. By understanding how melatonin works, how to use it effectively, and how much melatonin dosage you should take, individuals can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being.
XI AN CHEN LANG BIO TECH supply high quality melatonin and best melatonin price, please send inquiry to Email: [email protected] if you want to buy melatonin.

